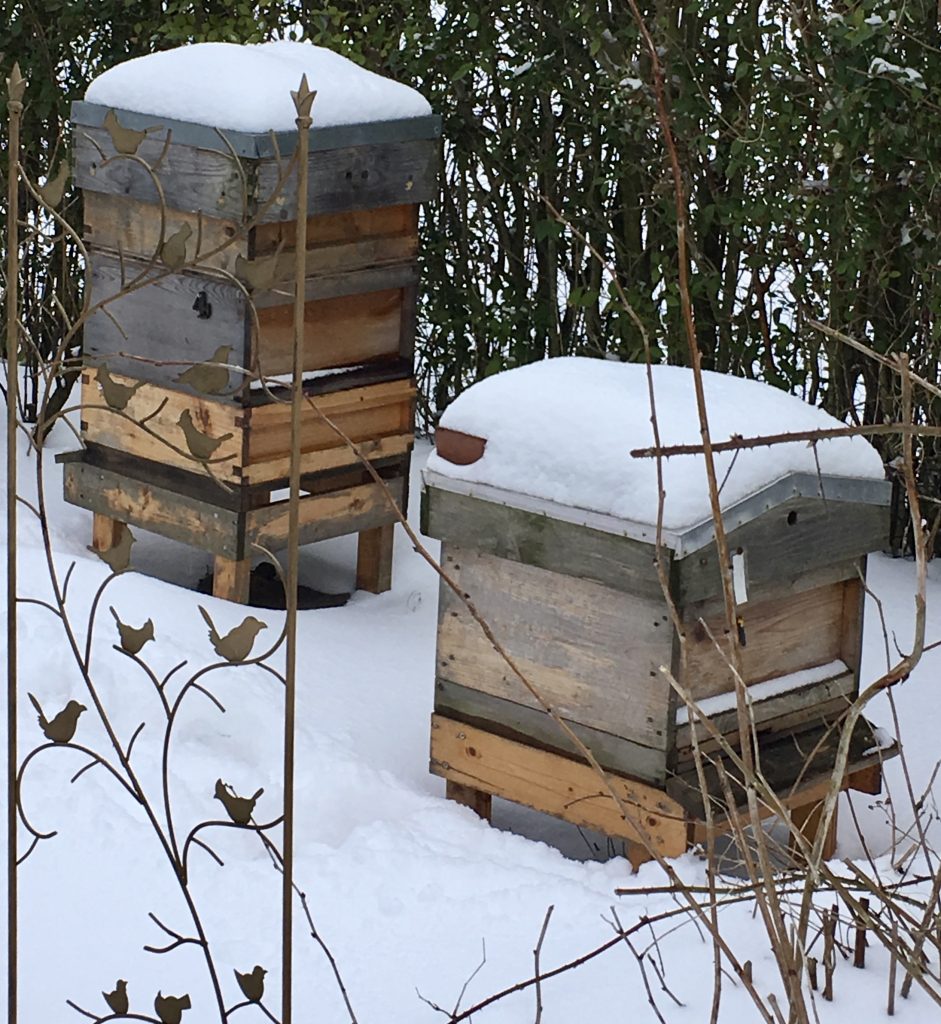
I’m often asked what happens to bee colonies in the winter. Well for many bees and wasps only the queens live through the winter. However, honey bees are different as they remain active all year around.
At this time of year the drones (male bees) get kicked out of the hive. This may seem harsh but they are no longer needed and would just consume valuable honey stores. As the weather gets cooler there is less nectar and pollen around. The number of bees in the colony reduces from the summer peak of 50-60,000 down to fewer than 10,000.
The bees form a cluster around the queen and her brood nest. They keep warm by eating their honey stores and ‘shivering’ their wing muscles keeping the centre of the nest at a toasty 37oc. On a warmer day the worker bees will fly out on ‘cleansing flights’ staining any washing or newly washed cars in the neighbourhood!
For beekeepers this is a quieter, more relaxing time of year. For the bees it is a very critical time. Colonies can easily starve if they get isolated from their honey stores. Each year the British Beekeepers Association monitors colony losses.
For both bees and beekeepers we wait for the first signs of snowdrops and crocus to signal the start of spring and a new year ahead.